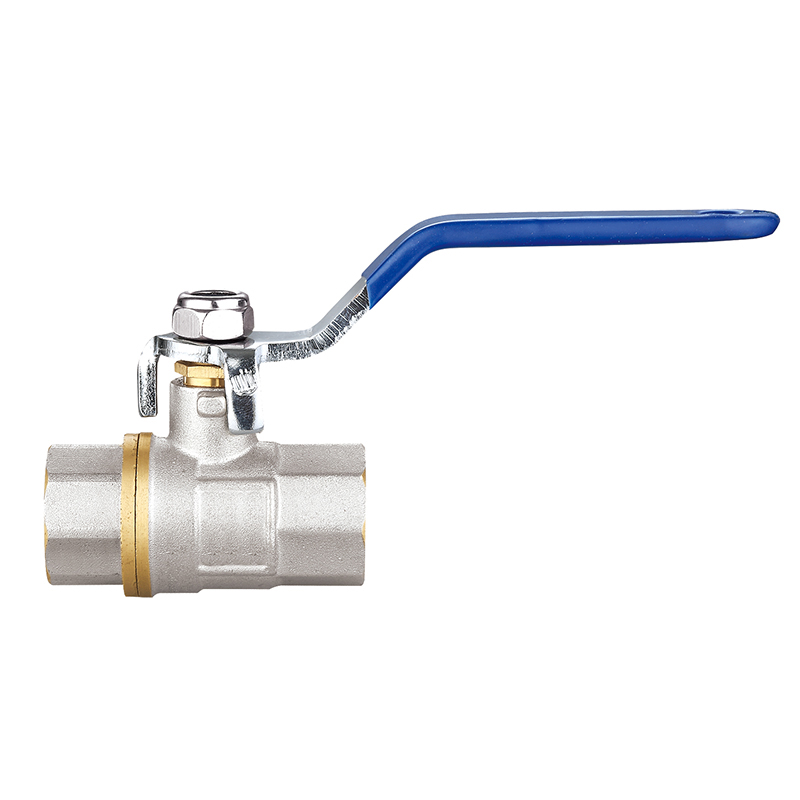
Foot Valves: Essential Check Valves for Reliable Pump Suction and Flow Retention
2025-07-11
Foot valves are critical components in fluid handling systems, particularly in applications involving suction pumps, water wells, and irrigation networks. Installed at the lower end of a suction line, a foot valve functions as a one-way check valve that allows water to be drawn into the system while preventing it from flowing back out when the pump stops. This ability to maintain pump prime and consistent flow makes foot valves indispensable for ensuring system efficiency and preventing unnecessary wear on pumping equipment.
Unlike standard check valves, foot valves typically feature an integrated strainer or screen that prevents debris from entering the suction line, protecting both the valve mechanism and the pump itself. This dual functionality—non-return flow control and filtration—makes the foot valve a uniquely effective and reliable solution in both residential and industrial settings.
How Foot Valves Work
Foot valves operate using simple mechanical principles. When a pump is turned on, it creates suction in the inlet line, reducing pressure inside the pipe. This pressure differential causes the foot valve’s internal flapper or ball mechanism to open, allowing water to enter from the source (such as a well, tank, or river).
When the pump is turned off, the loss of suction allows gravity and reverse pressure to push the valve shut, sealing the inlet and preventing water from flowing backward. This function is especially important in vertical suction lines where backflow would otherwise drain the pipe and require the pump to be re-primed for each cycle—a time-consuming and potentially damaging process.
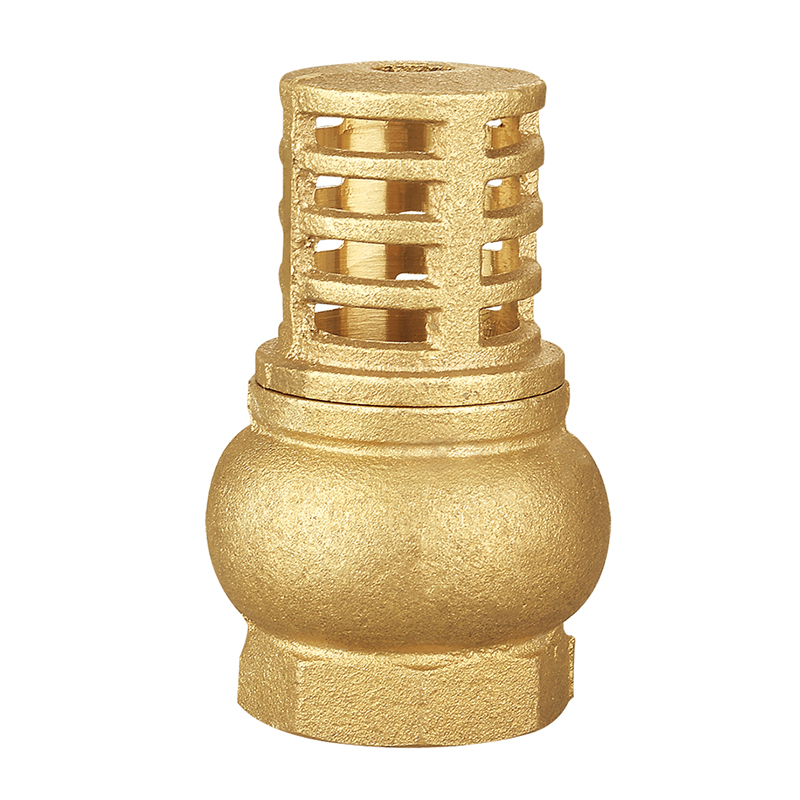

Key Components and Construction
A typical foot valve consists of the following elements:
Valve Body: Made of materials such as brass, stainless steel, PVC, or cast iron, depending on the application and fluid type.
Check Mechanism: This may be a flapper-style disc, spring-loaded ball, or swing mechanism that opens and closes based on fluid movement.
Strainer Screen: A perforated or mesh casing that surrounds the valve to block debris such as leaves, sand, and pebbles from entering the system.
Sealing Components: Rubber or polymer seats ensure a tight seal when the valve closes, leakage and maintaining suction.
High-quality foot valves are designed for durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of maintenance, ensuring they function reliably even in harsh or debris-laden environments.
Materials and Sizing Options
Foot valves are available in a wide range of materials and sizes to suit various flow capacities and installation needs:
Brass Foot Valves: Durable and corrosion-resistant, often used in agricultural and domestic well systems.
Stainless Steel Foot Valves: Ideal for industrial use and corrosive environments such as seawater applications or chemical pumping systems.
PVC Foot Valves: Lightweight and cost-effective, commonly used in irrigation, fish farms, and other non-metallic piping systems.
Cast Iron Foot Valves: Heavy-duty options used in municipal, construction, or large-scale water transfer projects.
Sizes typically range from 1/2 inch to 12 inches or more, with thread or flange connections compatible with standard piping systems.
Applications of Foot Valves
Foot valves are used wherever suction pumps draw water or fluid from a static source. Common applications include:
Water Wells: Prevents loss of suction and keeps the pump primed by holding water in the vertical inlet line.
Irrigation Systems: Maintains steady flow in agricultural setups, protecting pumps from dry-running and debris ingress.
Rainwater Harvesting: Ensures stored water remains available for pumping without backflow or clogging.
Industrial Water Systems: Keeps process water available for reuse or circulation in cooling and treatment systems.
Fountain and Pond Systems: Maintains consistent water draw for decorative or aeration purposes.
Fire Fighting and Emergency Pumps: Ensures readiness and quick draw from water tanks or external sources.
Benefits of Using Foot Valves
Prevents Backflow: Maintains suction and prevents the line from draining, which reduces pump priming cycles and startup time.
Protects Pumps: Reduces the risk of dry-running, cavitation, and internal wear.
Filters Debris: Integrated strainers keep harmful particles from entering the pump or clogging the pipeline.
Enhances System Efficiency: Helps maintain steady water pressure and flow, improving the overall performance of the fluid system.
Low Maintenance: Simple design allows for easy inspection and replacement when necessary.
Whether you want to become our partner or need our professional guidance or support in product selections and problem solutions, our experts are always ready to help within 12 hours globally.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى