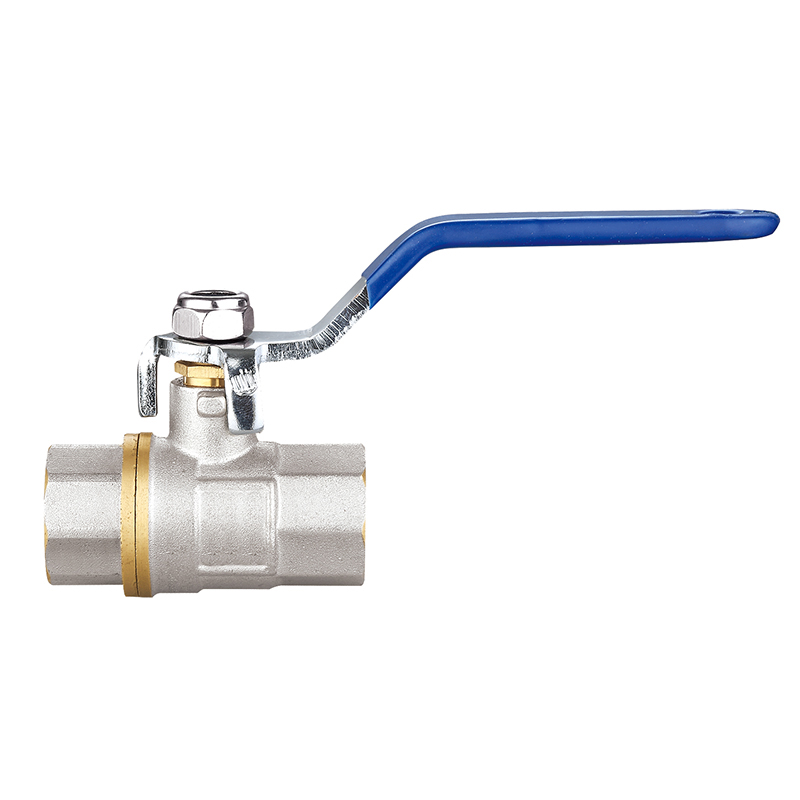
Foot Valves: Safeguarding Pumping Systems with Reliable Bottom-Line Protection
2025-07-11
In the realm of fluid control and pumping systems, one often-overlooked yet vital component is the foot valve. Installed at the bottom of a suction line inside a tank, reservoir, or well, foot valves serve a dual purpose: allowing fluid to enter the pump suction line while preventing backflow. Their role is crucial in maintaining pump prime, protecting the system from damage, and ensuring continuous, efficient operation.
As industries and municipalities push for more resilient and efficient pumping infrastructure, the humble foot valve is gaining renewed attention—especially as innovations in materials and design make it more reliable and adaptable than ever.
What Is a Foot Valve and How Does It Work?
A foot valve is a type of check valve installed at the intake of a pump’s suction pipe. It allows liquid to flow upward into the pipe when the pump operates, but automatically closes when the pump stops. This prevents the fluid from draining back down, thereby maintaining a primed pump condition—critical for systems like irrigation, municipal water supply, and industrial processes where downtime can be costly.
What differentiates foot valves from standard check valves is the presence of a screen or strainer that filters out debris and prevents clogging. This self-cleaning design not only protects the pump but also reduces the need for upstream filtration.
Key Benefits of Using Foot Valves
Pump Protection and Longevity
By maintaining prime and preventing dry running, foot valves extend the life of pumps and reduce the risk of mechanical failure.
Energy Efficiency
When pumps remain primed, they require less energy to start and operate. This translates into reduced power consumption and operational costs over time.
Reduced Maintenance Downtime
Foot valves help eliminate the need for frequent manual priming, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming—especially in remote or hard-to-reach installations.
Improved System Reliability
Inconsistent fluid delivery and air pockets in piping can disrupt operations. Foot valves stabilize flow and pressure, improving system performance.
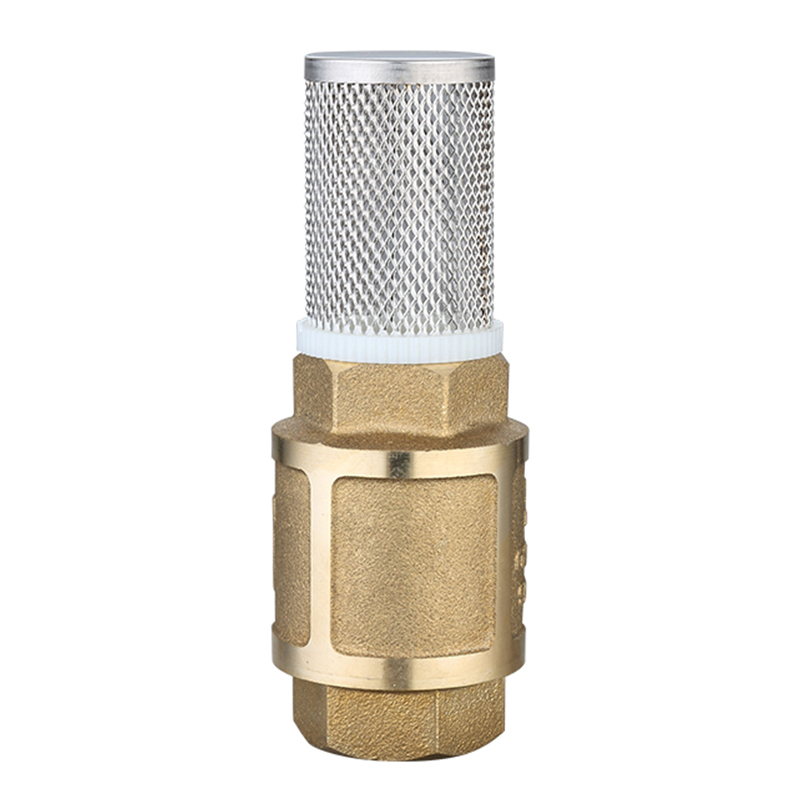

Material Matters: Durability in Demanding Conditions
Modern foot valves are constructed using high-performance materials that ensure long service life and maintenance, even in harsh or corrosive environments. Common options include:
Stainless Steel: Offers corrosion resistance, making it ideal for seawater, chemical, or wastewater applications.
Brass: A reliable choice for general-purpose water systems, offering a good balance of strength and resistance to mineral buildup.
PVC or Polypropylene: Lightweight and cost-effective options for agricultural or light-duty systems with non-corrosive fluids.
Many designs also incorporate rubber or PTFE seals, enhancing tight shutoff capabilities and preventing leakage during operation.
Versatile Applications Across Industries
Foot valves are indispensable across various sectors:
Agriculture and Irrigation: Used in pump-driven irrigation systems to prevent back-siphoning and ensure consistent water delivery to crops.
Municipal Water Systems: Help maintain pump integrity in potable water extraction from wells or reservoirs.
Industrial and Chemical Plants: Installed in tanks and process vessels where fluid must be reliably drawn without risk of contamination or backflow.
Mining and Construction: Employed in dewatering pumps that operate in abrasive, sediment-laden water.
Each of these applications requires a customized approach based on flow rate, fluid characteristics, and environmental conditions—emphasizing the importance of proper foot valve selection.
Design Advancements Improving Performance
To meet the increasing demand for high-efficiency, low-maintenance components, manufacturers are introducing a range of innovative features:
Self-Cleaning Screens: Some foot valves feature anti-clogging mesh designs that reduce maintenance intervals.
Spring-Loaded Closure Mechanisms: Enhances responsiveness during shutdown, reducing the risk of fluid loss or backflow contamination.
Modular Construction: Allows for easy disassembly, inspection, and replacement of parts, simplifying service in the field.
Low-Pressure Drop Designs: Minimize resistance to fluid entry, boosting overall pump efficiency.
Installation Practices
For performance, proper installation of foot valves is essential:
Secure Positioning: The valve must be fully submerged in fluid and mounted vertically to ensure correct function.
Clearance from the Bottom: Installing the valve several inches above the tank or well bottom prevents sediment intake.
Regular Inspection: Periodic cleaning of the strainer and checking for seal wear helps extend the valve’s operational life.
These practices, combined with quality materials, help foot valves perform reliably even under continuous or demanding service conditions.
Whether you want to become our partner or need our professional guidance or support in product selections and problem solutions, our experts are always ready to help within 12 hours globally.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى