Water Valve Systems: A Detailed Overview of Types and Applications
2025-07-11
Water valves are indispensable components in modern plumbing and fluid control systems. They serve as regulators, flow controllers, and safety devices in residential, commercial, and industrial water supply infrastructures. The term "water valve" encompasses a broad range of specialized valves, each tailored to specific roles in the system. This includes ball valves, faucets, angle valves, stop valves, check valves, and valve joints. Each of these plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth and controlled movement of water throughout various installations.
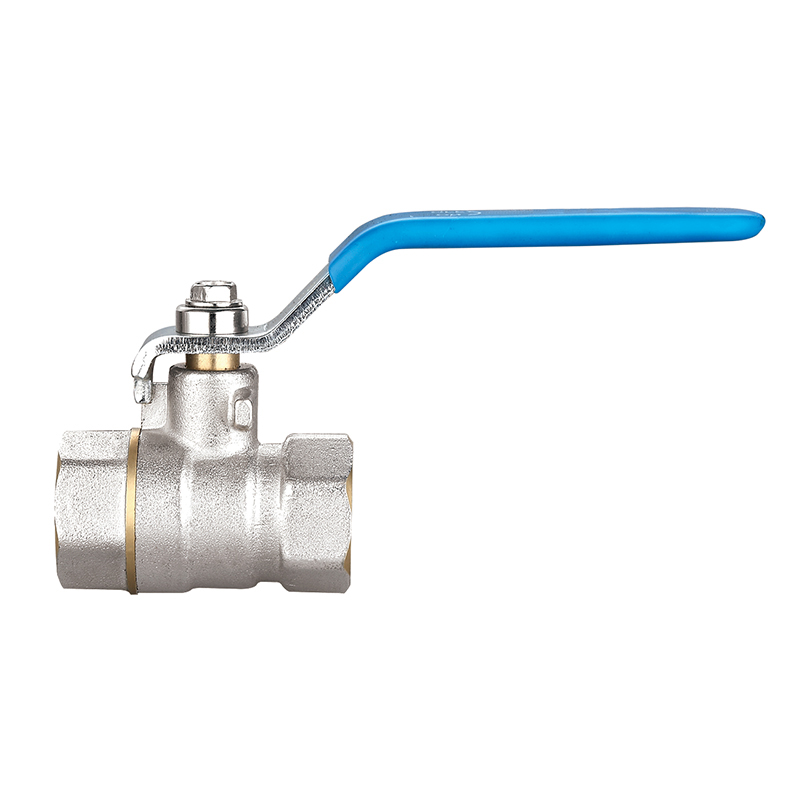
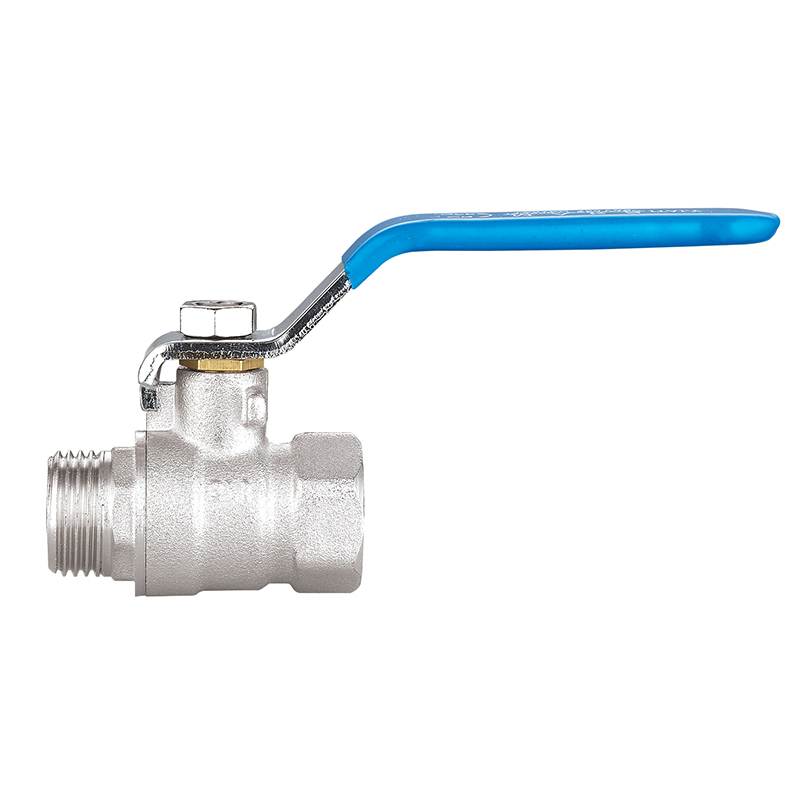
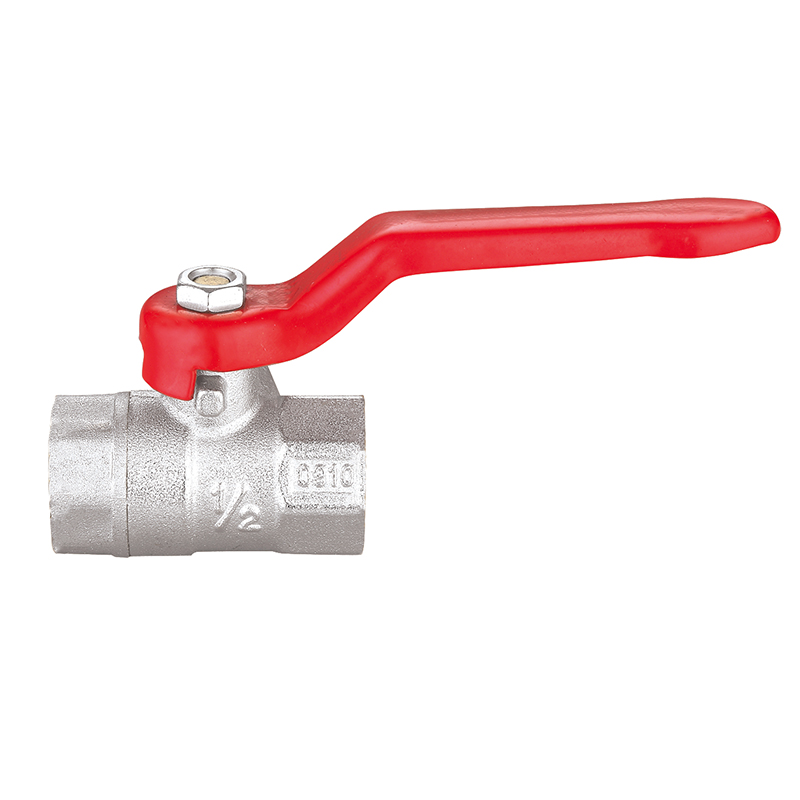
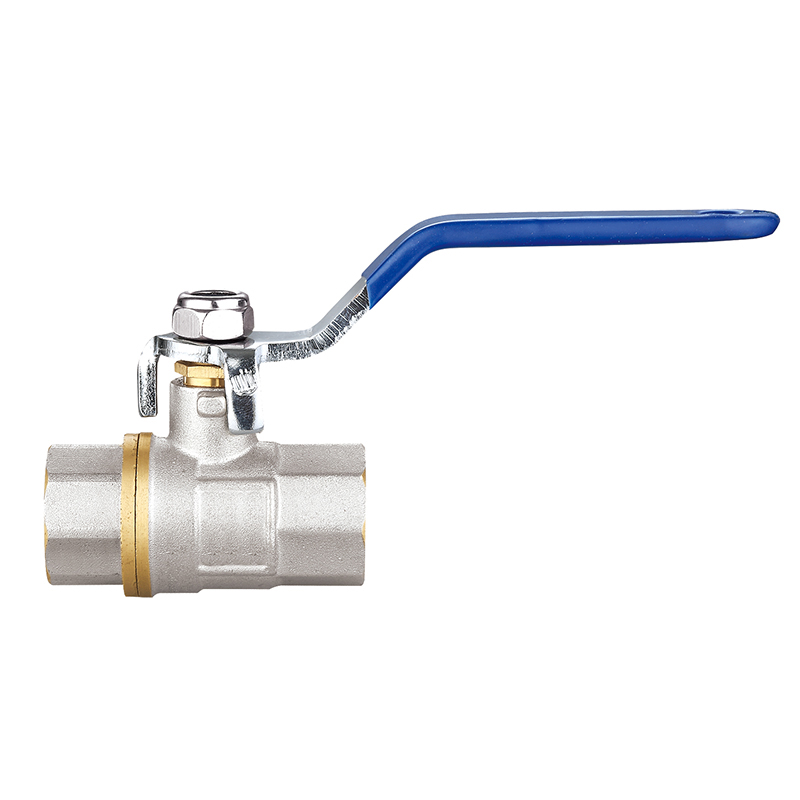
Ball Valves
Ball valves are widely recognized for their simplicity, efficiency, and tight sealing capabilities. They consist of a rotating ball with a central bore that aligns with the pipeline when the valve is open and blocks flow when turned perpendicular. A quarter-turn operation makes them extremely user-friendly while delivering instant shutoff functionality.
Due to their reliability and low maintenance needs, ball valves are used in both residential plumbing systems and heavy-duty industrial environments. They are ideal for high-pressure applications and systems where full flow or full shutoff is essential. The durable construction—often in brass, stainless steel, or PVC—enhances longevity, even under challenging operating conditions.
Faucets
Faucets are the visible and user-interactive type of water valve. Positioned at the termination point of water lines, faucets control the release of water for everyday use. Whether in kitchens, bathrooms, laundry rooms, or gardens, they serve as the primary interface between the plumbing system and the user.
Modern faucets have evolved significantly to offer features such as dual-handle mixing, ceramic disc cartridges for longevity, aerators for water conservation, and sensor-based activation for hygiene. Aesthetic design also plays a major role in faucet selection, as these fixtures must harmonize with the surrounding décor while delivering dependable functionality.
Angle Valves
Angle valves, also known as corner valves, are compact water valves designed for spaces where pipes meet fixtures at a 90-degree angle. Typically installed beneath sinks, behind toilets, and near washing machines, angle valves provide a critical point of control for specific water outlets.
These valves are essential for service and maintenance purposes, allowing users to shut off water to individual fixtures without disrupting the entire plumbing network. Constructed from corrosion-resistant materials like chrome-plated brass, angle valves offer both aesthetic appeal and lasting performance in environments prone to moisture.
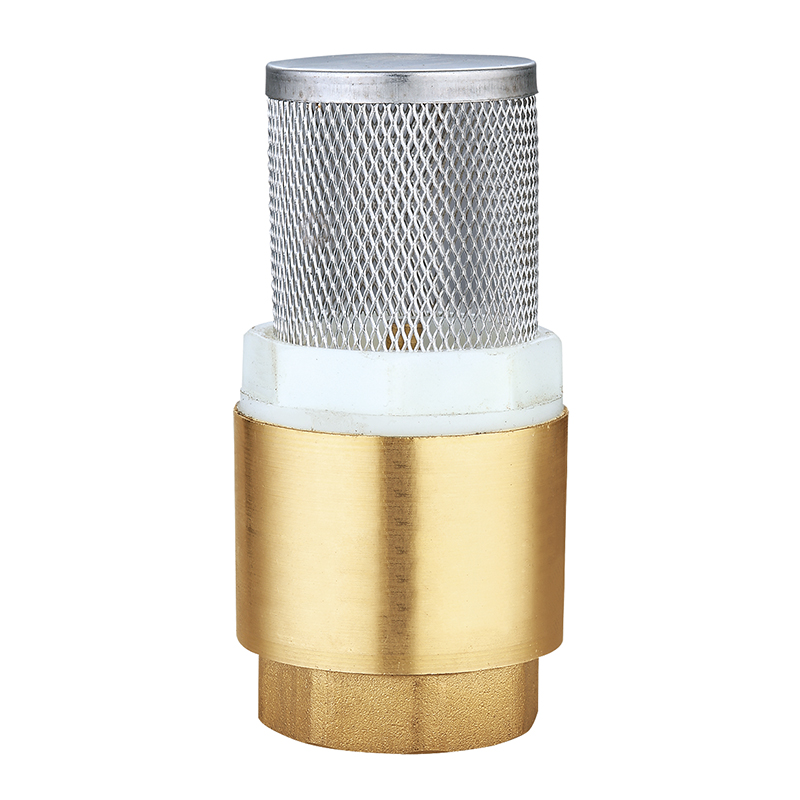

Stop Valves
Stop valves perform the key function of isolating parts of a water supply system for maintenance or emergencies. Unlike ball valves, which are operated with a quarter turn, stop valves generally use a rising or non-rising stem that requires multiple turns to open or close. This allows for finer control over the water flow.
Stop valves are commonly installed on branch lines to specific fixtures, such as toilets, sinks, and water heaters. Their precise control and durability make them ideal for residential plumbing systems. They are also valuable in commercial applications, such as in office buildings or public restrooms, where localized control is needed.
Check Valves
Check valves are automatic devices that allow water to flow in one direction only. Their main purpose is to prevent backflow, which can cause contamination or pressure issues in the system. These valves are especially important in systems that involve pumps, vertical pipe runs, or where water needs to flow uphill.
There are several types of check valves, including swing, lift, and spring-loaded versions. Each is chosen based on the application’s pressure, flow rate, and orientation. Common use cases include well pumps, HVAC systems, fire sprinkler systems, and irrigation networks. Their maintenance-free operation adds to their value in both small- and large-scale plumbing systems.
Valve Joints
Valve joints are the connectors that link valves to the rest of the plumbing system. Their role is critical in ensuring leak-free, secure installations that can withstand pressure and thermal expansion. Valve joints vary by connection type, including threaded, soldered, flanged, and push-fit designs.
Choosing the right valve joint depends on the material of the pipe (copper, PVC, PEX, etc.), installation requirements, and the nature of the system (pressurized or gravity-fed). A properly installed valve joint not only ensures efficient water flow but also contributes to the overall safety and longevity of the plumbing system.
Whether you want to become our partner or need our professional guidance or support in product selections and problem solutions, our experts are always ready to help within 12 hours globally.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى