Pipe Fittings: The Unsung Connectors Behind Efficient Piping Systems
2025-07-11
In the global infrastructure of plumbing, HVAC, oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment systems, one category of components often goes unnoticed—yet it is absolutely critical to performance, safety, and efficiency. These are pipe fittings, the small but essential connectors that bring entire piping systems together.
While valves control the flow and pipes carry the media, pipe fittings ensure the proper direction, connection, and sealing of fluids and gases. The proper selection, sizing, material choice, and installation of these components directly impacts the reliability, energy efficiency, and safety of entire systems.
What Are Pipe Fittings?
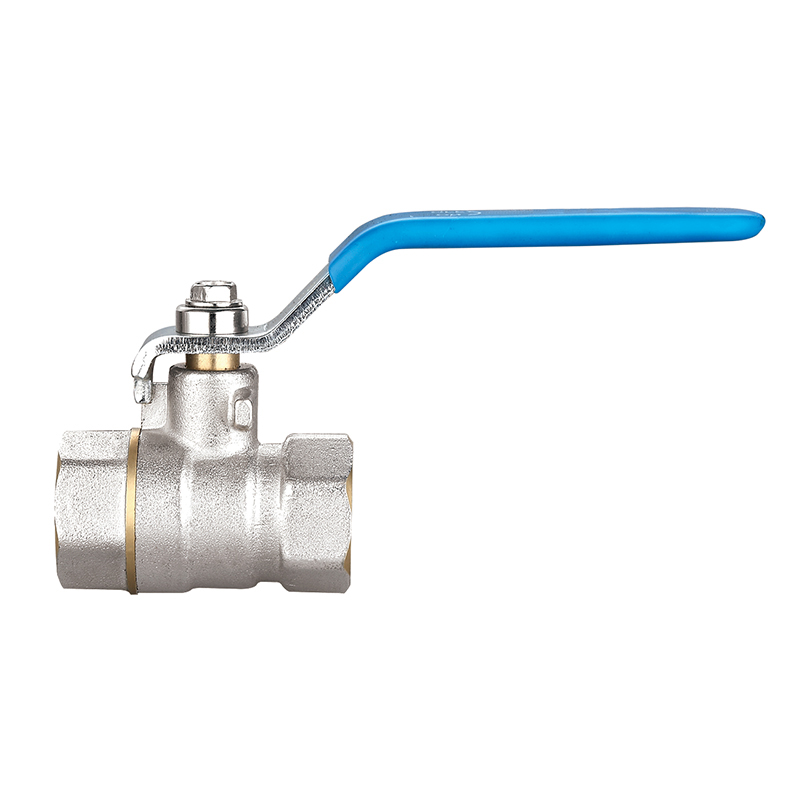
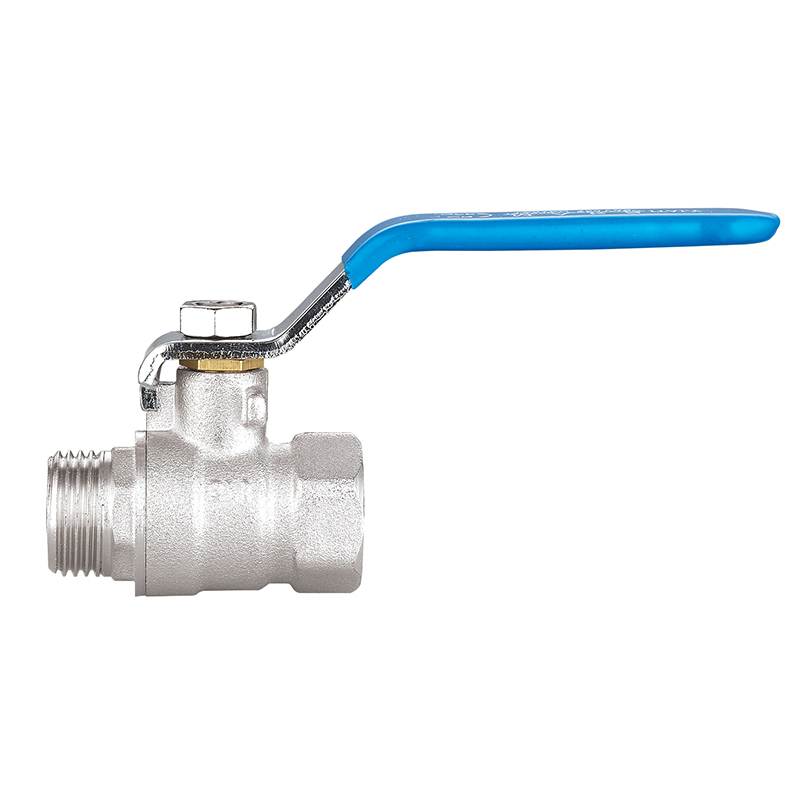
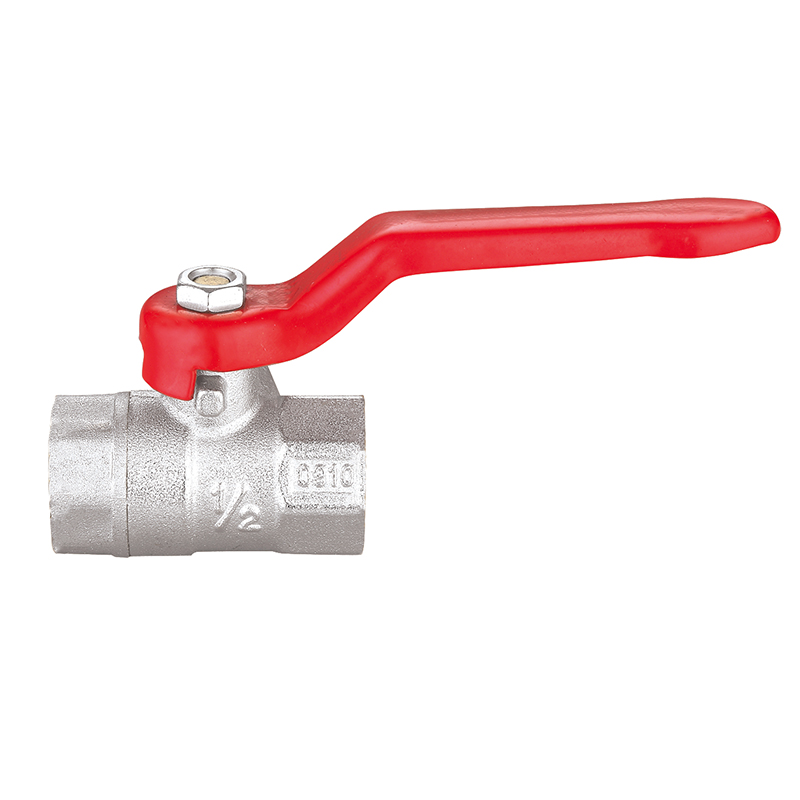
Pipe fittings are devices used to connect different sections of piping, change direction or diameter, split or merge flows, and provide access for inspection or maintenance. They come in a wide variety of shapes and functions, including:
Elbows (90°, 45°): Change the direction of flow.
Tees and Crosses: Split flow into multiple directions.
Reducers and Expanders: Change pipe diameter.
Couplings and Unions: Join straight sections of pipe.
Caps and Plugs: Close off the ends of pipe systems.
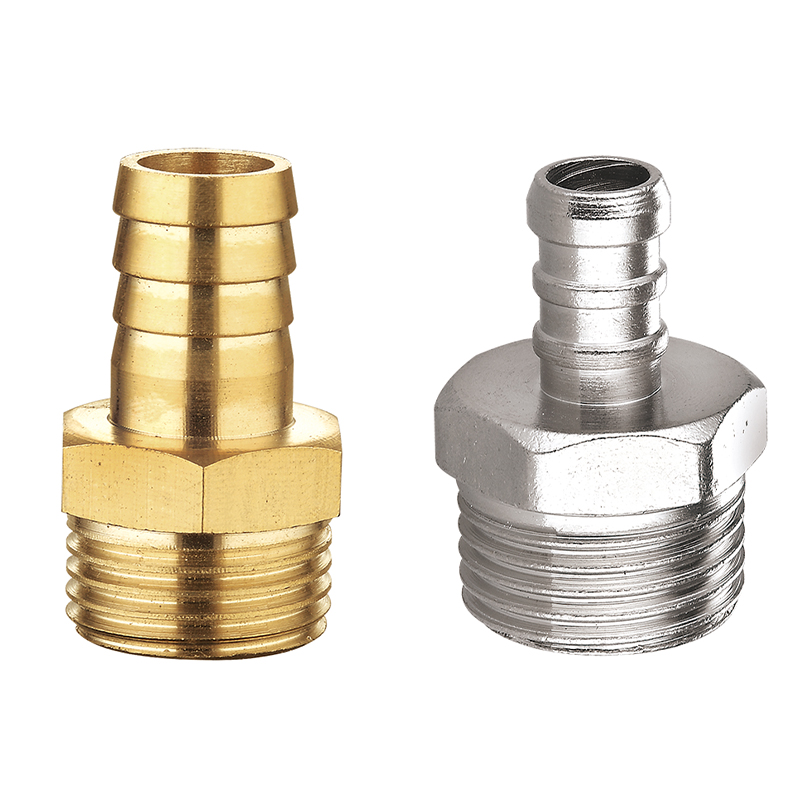
Adapters and Bushings: Connect different pipe types or sizes.
Each type of fitting plays a specific role in creating a fully functional and leak-proof piping network.
Why Proper Selection Matters
The success of a piping system doesn’t just depend on the pipe itself—it hinges on the quality and compatibility of the fittings used. Choosing the wrong fitting can result in leaks, pressure losses, system inefficiency, or catastrophic failure.

Key factors that influence fitting selection include:
Material compatibility: Fittings must be chemically and thermally compatible with the pipe and the fluid being transported.
Pressure and temperature ratings: Every fitting must be able to withstand the system’s operating conditions.
Connection method: Threaded, welded, flanged, push-fit, or compression fittings each have unique advantages and use cases.
Corrosion resistance: For systems exposed to moisture, chemicals, or saltwater, materials like stainless steel or PVC may be over mild steel or brass.
For instance, using galvanized steel fittings in a system transporting corrosive chemicals could result in rapid degradation and dangerous leaks. Similarly, failing to use pressure-rated fittings in a high-pressure steam system could lead to system failure or even injury.
Installation Quality: A Critical Step
Even the pipe fittings will fail if not installed correctly. Installation techniques must match the specific type of fitting and follow proper torque, sealing, and alignment practices. Some of the common causes of system failures include:
Over-tightening threaded fittings, which can crack or deform the threads.
Improper welding or brazing, to weak joints or warping.
Misaligned pipes, which place strain on joints and fittings, increasing the risk of failure.
Insufficient sealing materials like thread tape or joint compound in threaded fittings.
Regular training, use of specialized tools, and adherence to manufacturer specifications can dramatically improve the quality and longevity of installations.
Pipe Fitting Materials: Choosing the Right One
Pipe fittings are made from a range of materials to suit different applications:
Copper: Widely used in domestic plumbing and HVAC systems due to its thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Brass and Bronze: Ideal for potable water systems thanks to their resistance to corrosion and dezincification.
Stainless Steel: Offers strength and corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments and hygienic applications.
Carbon Steel: Used in high-pressure industrial applications, though it requires corrosion protection.
PVC and CPVC: Lightweight, cost-effective, and suitable for cold and hot water, respectively.
Polyethylene (PE) and PP-R: Popular in modern plumbing and industrial piping for their chemical resistance and fusion-welded connections.
Each of these materials has unique pressure, temperature, and chemical resistance characteristics, making material selection a foundational step in system design.
Applications in Every Industry
From residential plumbing to massive industrial plants, pipe fittings are everywhere:
Water and wastewater systems use corrosion-resistant fittings to ensure sanitary operation and longevity.
Oil and gas pipelines rely on high-pressure steel fittings, often welded, to maintain integrity over long distances.
Food and beverage processing requires stainless steel fittings to meet hygiene regulations.
HVAC systems use a combination of copper, brass, and plastic fittings for efficient thermal transfer and fluid circulation.
Fire protection systems rely on robust fittings that maintain system pressure in emergencies.
Whether you want to become our partner or need our professional guidance or support in product selections and problem solutions, our experts are always ready to help within 12 hours globally.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى